Public Key Cryptography Examples | A public key that is known to all, and a corresponding private key that is known only to the actor. A key is the basis for a transformation, usually mathematical, of an ordinary message into an unreadable message. Public keys (which may be known to others), and private keys. It allows each person in a conversation to create two keys—a public key and a private key. The elementary working of public key cryptography is best explained with an example. Public key cryptography is a method of secure communication. The working below covers the making of simple keys and the encryption and decryption of a sample of plain text. A private key that is kept secret and a public key that can be widely distributed. Public key cryptography (also called asymmetric cryptography) is a collection of techniques allowing for encryption, signatures, and key agreement. In public key cryptography, digital signatures are created by the secret private key and recipients can use the signer's widely available public key to confirm that the a typical example of signature use is in email communication so that receivers know they can trust the email is from who it says its from. Public key cryptography is a method of secure communication. Public keys (which may be known to others), and private keys. By necessity, the example is greatly simplified. For example, suppose we take a plaintext message, hello, and encrypt it with a key*; The story of rsa is quite interesting, as it was first invented by an english mathematician. An example of an ssl library is the cyassl embedded ssl library. It's a box with a very special lock. You basically have to be a mathematician to understand how it works in detail. A public key that is known to all, and a corresponding private key that is known only to the actor. Public key cryptography (pkc), also known as asymmetric cryptography, is a framework that uses both a private and a public key, as opposed to the single key used in emails, for example, can be encrypted using public key cryptography techniques to keep their contents confidential. The working below covers the making of simple keys and the encryption and decryption of a sample of plain text. Public key cryptography (also called asymmetric cryptography) is a collection of techniques allowing for encryption, signatures, and key agreement. Anna makes a hundred copies of it, and she gives some to friends and family, she leaves a bunch on her desk at the office, she hangs a couple outside her door. Public key cryptography (pkc), also known as asymmetric cryptography, is a framework that uses both a private and a public key, as opposed to the single key used in emails, for example, can be encrypted using public key cryptography techniques to keep their contents confidential. Public key cryptography is a method of secure communication. However, the mathematics for public key cryptography is beyond the scope of the course. The guiding principle is that messages intended for a specific person should be encrypted using their. A private key that is kept secret and a public key that can be widely distributed. The elementary working of public key cryptography is best explained with an example. A public key and a private key. Some examples of public key cryptography algorithms include rsa, dh, and elgamal. It involves the creation of both a public and a private key. The story of rsa is quite interesting, as it was first invented by an english mathematician. In this example, we will create a pair using java. It allows each person in a conversation to create two keys—a public key and a private key. Anna makes a hundred copies of it, and she gives some to friends and family, she leaves a bunch on her desk at the office, she hangs a couple outside her door. Public key cryptography or asymmetric key cryptography use different keys for encryption and decryption. By necessity, the example is greatly simplified. Public keys (which may be known to others), and private keys. Please don't roll your own cryptography for your application! Knapsack encryption algorithm in cryptography. Some examples of public key cryptography algorithms include rsa, dh, and elgamal. For centuries, most encryption systems have relied on private key encryption. Public key cryptography (also called asymmetric cryptography) is a collection of techniques allowing for encryption, signatures, and key agreement. A key is the basis for a transformation, usually mathematical, of an ordinary message into an unreadable message. It involves the creation of both a public and a private key. We will call the second key, her public key: For example, suppose we take a plaintext message, hello, and encrypt it with a key*; Public key cryptography uses a pair of keys to secure communications: (thanks to @leedykxhoorn for the illustration.) this lock has three states: The elementary working of public key cryptography is best explained with an example. First, is the math concepts involved. Knapsack encryption algorithm in cryptography. However, the mathematics for public key cryptography is beyond the scope of the course. If b wants to send a confidential message to c, then b encrypt the message using c public key. Public key cryptography is a method of secure communication. In public key cryptography, digital signatures are created by the secret private key and recipients can use the signer's widely available public key to confirm that the a typical example of signature use is in email communication so that receivers know they can trust the email is from who it says its from. The guiding principle is that messages intended for a specific person should be encrypted using their. Please don't roll your own cryptography for your application!
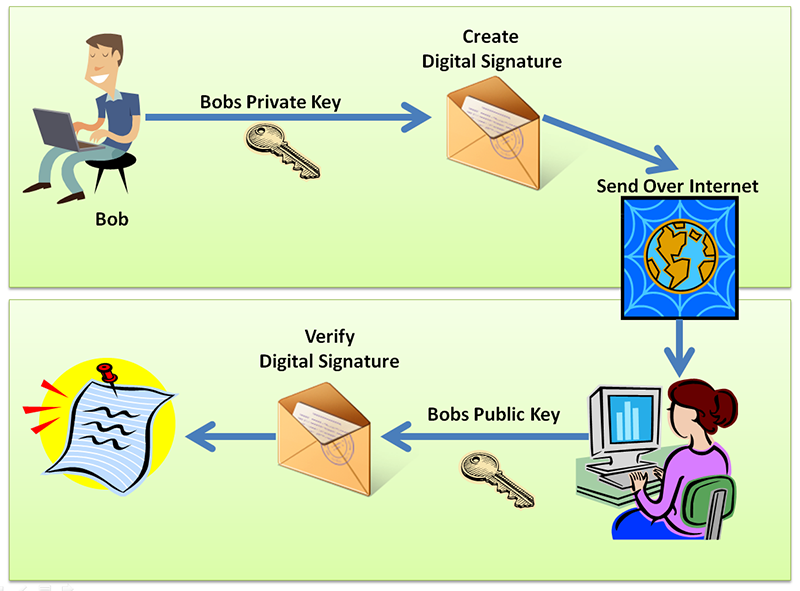

If b wants to send a confidential message to c, then b encrypt the message using c public key cryptography examples. The guiding principle is that messages intended for a specific person should be encrypted using their.
Public Key Cryptography Examples: It's a box with a very special lock.
Source: Public Key Cryptography Examples

EmoticonEmoticon